How To Remove Old Reminents Of Uninstalled Software Before Clean Install
Introduction
This tutorial will walk you through several methods for removing software packages from an Ubuntu Linux system. We particular removal options using the GUI (graphical user interface) built in to the Ubuntu Software Center and using the command line.
Prerequisites
- A user account with sudo / administrative privileges to install/uninstall software from Ubuntu
- Access to a last window/control line (Ctrl+Alt+T) – optional
7 Ways to Uninstall Ubuntu Packages
Remove With Ubuntu Software Director
If you run Ubuntu with the default graphical interface, you may be familiar with the default software director. This graphical tool gives a list of bachelor and installed programs. Launch it by clicking the Ubuntu Software Center icon.

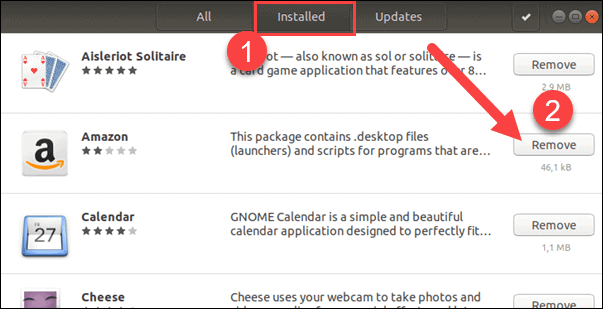
One time the utility loads, there are iii tabs beyond the height:
- All – This lists all bachelor software. Yous can search this list for new programs to add.
- Installed – This lists merely the programs y'all have installed.
- Updates – This lists any programs that have bachelor updates. Y'all can find more than information about the updates from hither.
Click the Installed tab. Gyre downwardly the list of programs, then click the Remove push button next to the program to uninstall.
Use the Synaptic Package Manager
The default Ubuntu Software Center may not display every application on your organization. The Synaptic Package Director is a more robust application. The Synaptic Parcel Director is included by default in some versions of Ubuntu. Use the search bar to observe and launch it on your system.
If your system does not include Synaptic Parcel Manager, use the Ubuntu Software Heart to install it.
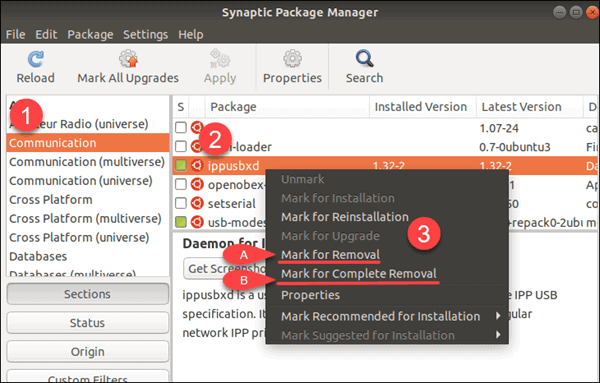
Once the Synaptic Package Manager loads, use the bill of fare on the left to select Status > Installed. This lists all applications on your system.
To remove an application, highlight it > right-click > select Mark for Removal and then click Apply. This will uninstall the software, but go out the configuration files intact.
To delete the standard configuration files along with the software package, select Marker for Complete Removal instead.
How to Remove Package on Ubuntu From Command Line
Dpkg (Debian Package) is a standard package manager in many versions of Linux. To uninstall a packet with the dpkg command, y'all demand to know the exact proper name of the package y'all intend to uninstall.
To listing installed packages enter the post-obit into a terminal window:
sudo dpkg ––list This command lists all the software, but the list may be also long and not helpful.
To make a listing easier to browse add the following:
sudo dpkg–query –l | less If you know the proper name of the packet you want to remove, y'all can search for it instead:
sudo dpkg–query –50 | grep package_name Supervene upon package_name with the term you are searching for.
If you don't know the full name, specify part of a name by surrounding it with asterisks (*), as follows:
sudo dpkg–query –l | grep *partial_name* We advise copying the verbal software bundle name (right click and re-create) for use later on in the removal process.
Notation: Using dpkg to remove software packages is not recommended. The recommended option is to employ a package manager that will remove all dependencies. For example, dpkg may remove the specified bundle, only all of its dependencies will remain on the arrangement and may no longer office correctly.
Apt-Become Remove Control
To remove a specific package, apply the apt-get remove command:
sudo apt-get remove package_name This control prompts apt to scan through the installed applications and attempt to remove or repair any that are broken.
Apt-Get Purge Command
Supplant package_name with the actual package name generated by apt or dpkg.
The remove command only deletes the software, not the configuration files.
To remove the program and config files, use the purge command:
sudo apt-get remove ––purge package_name Clean Command
The apt package director can too clean upwards your system.
To delete the cache of onetime/outdated packages, enter:
sudo apt-become clean Some programs are installed with dependencies. These are other software packages the program needs to run. It's possible to uninstall an application, and still have all its dependencies on your arrangement.
This command prompts apt to scan through the installed applications and effort to remove or repair whatsoever that are broken.
AutoRemove Control
The apt package manager tin can remove orphaned or unnecessary dependencies with autoremove :
sudo apt-get autoremove If you have any failed installations, broken dependencies, or corrupted bundle files, apt tin try to repair them with the command:
sudo apt-go –f install This command prompts apt to scan through the installed applications and endeavour to remove or repair whatsoever that are broken.
Determination
Now y'all should take a skilful agreement of several means to find and remove packages on Ubuntu Linux.
Was this commodity helpful?
Yeah No
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/uninstall-packages-programs-ubuntu
Posted by: flavinberighbour.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Remove Old Reminents Of Uninstalled Software Before Clean Install"
Post a Comment